

Labels: Operating system 0 comments
Morph OS
at 8:33 AM Posted by Sni
MorphOS is a lightweight, media-centric OS build to run on PowerPC processors. It is inspired by AmigaOS and also includes emulation to be able to run Amiga applications.

Source model: Closed source
License: Mixed proprietary and open source
Platform: Pegasos, some Amiga models, EFIKA.
Labels: Operating system 0 comments
Sky OS
at 8:30 AM Posted by Sni

Source model: Closed source
License: Proprietary
Platform: x86
State: Beta
Labels: Operating system 0 comments
Syllable desktop
at 8:28 AM Posted by Sni
Syllable is a free and open source operating system that was forked in 2002 from AtheOS, an AmigaOS clone. It’s intended as a lightweight and fast OS suitable for home and small office users.

Source model: Free and open source
License: GNU General Public License
Platform: x86
State: Alpha
React OS
at 5:44 AM Posted by Sni
ReactOS is an operating system designed to be compatible with Microsoft Windows software. The project started in 1998 and today it can run many Windows programs well. The ReactOS kernel has been written from scratch but the OS makes use of Wine to be able to run Windows applications.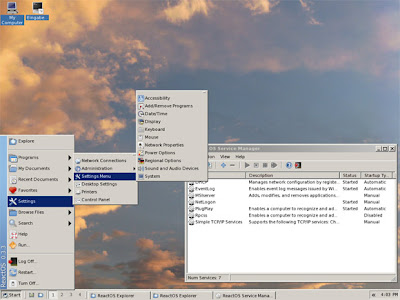
Source model: Free and open source
License: Various free software licenses
Platform: x86 (more under development)
State: Alpha
Labels: Operating system 0 comments
Heysan is VIRUSSSS !!!
Wednesday, November 12, 2008 at 3:40 AM Posted by Sni
Heysan Link :- Its spreading fast and lot of things appear to be changing..like contact list being deleted, people in your contact list recieving link to heysan.com as if you are sending it..and much more. Until we find some solution from Google, People please be advised nto to open suck links.

Though usually I'm highly suspicious of these sorts of clicks, I went ahead and clicked it. (After all, Firefox, my favourite web browser has quite a decent track record as far as security is concerned).The site that opened up looked like:

Haiku
Friday, November 7, 2008 at 11:57 PM Posted by Sni
Introduction :
Haiku is an open source project aimed at recreating and continuing the development of the BeOS operating system (which Palm Inc. bought and then discontinued). Haiku was initially known as OpenBeOS but changed its name in 2004.
Haiku is compatible with software written for BeOS.
Source model: Free and open source
License: MIT License
Platform: x86
PowerPCState: Pre-Alpha
Read more at the Haiku website.
Labels: Operating system, Technology 0 comments
AmigaOS 4.1
at 11:14 PM Posted by Sni
Introduction :
This month (September 2008) AmigaOS 4.1 was released .
Although AmigaOS is a veteran in the field (many have fond memories of the original Amiga computer), its current version is a fully modern OS. AmigaOS only runs on specific PowerPC-based hardware platforms . The company ACube is currently marketing and distributing AmigaOS and is going to bundle the OS with their motherboards.
PowerPC processor running at 400MHz or higher, 256 megabytes of RAM, 100 megabytes of hard drive space, and a Radeon 7000 video card. A Radeon 9250 is recommended, however, as AmigaOS 4.1 contains a new graphics subsystem that—like Windows Vista and Macintosh OSX—uses the card's 3D features for a graphics compositing layer.
The OS is solid and evolving, and there are many places it could go. The announcement of support for the SAM440 motherboards is just a start: there is a large existing base of PowerPC-based Macintoshes that could easily be made to run OS 4.1, and the low RAM requirements of the OS would make it perfect for running on Sony's PlayStation 3 or on any number of mobile platforms.
License: Proprietary
Platform: PowerPC
State: Final
Changing label of drives on UBUNTU desktop !!
Wednesday, November 5, 2008 at 6:47 AM Posted by Sni
Install mtools for FAT32 or FAT16 partition or ntfsprogs for NTFS .
After installing unamount whose label is to be renamed and run required utility as the root user.
Restart the computer.
Phishing !!!
at 6:38 AM Posted by Sni
Labels: internet 0 comments
Email Spam !!!
at 6:26 AM Posted by Sni
 Email Spam is a Form of net abuse, in which messaging systems indiscriminately send unsolicited bulk messages .
Email Spam is a Form of net abuse, in which messaging systems indiscriminately send unsolicited bulk messages .
Email Spoofing !!!!
at 6:14 AM Posted by Sni
E-mail spoofing is a term used to describe fraudulent e-mail activity in which the sender address and other parts of the e-mail header are altered to appear as though the e-mail originated from a different source.Is a technique commonly used for spam e-mail and phishing to hide the origin of an e-mail message. By changing certain properties of the e-mail, such as the From, Return-Path and Reply-To fields (which can be found in the message header), ill-intentioned users can make the e-mail appear to be from someone other than the actual sender. The result is that, although the e-mail appears to come from the e-mail indicated in the "From" field (found in the e-mail headers) it actually comes from another e-mail address, probably the same one indicated in the "Reply To" field; if the initial e-mail is replied to, the delivery will be sent to the "Reply To" e-mail, that is, to the spammer's e-mail.
Method :- The technique is now used ubiquitously by mass-mailing worms as a means of concealing the origin of the propagation. On infection, worms such as ILOVEYOU, Klez and Sober will often try to perform searches for e-mail addresses within the address book of a mail client, and use those addresses in the From field of e-mails that they send, so that these e-mails appear to have been sent by the third party. For example: User1 is sent an infected e-mail and then the e-mail is opened, triggering propagation The worm finds the addresses of User2 and User3 within the address book of User1 From the computer of User1, the worm sends an infected e-mail to User2, but the e-mail appears to have been sent from User3 .
Labels: internet, virus 0 comments
Installing XP over Vista !!!!
Tuesday, November 4, 2008 at 8:45 AM Posted by Sni
You need empty partition . To make one use computer management to resize existing partition and make space for a new one.
To resize partition :-
Go to disk management application . Righ Click on partition .
Click on shrink volume. Choose SPace.
Change drive letter or path to avoid confusion.
Right click on empty space created.
Click on new Simple volume.
Create partition with right click drive letter.
now --- > Boot using XP installation CD and install.
--- > You wont be able to boot into windows vista any longer.Boot into XP and install software called VistaBootPRO from www.vistabootpro.org which allows to make entry and changes to boot record.
Labels: Operating system, windows 0 comments
Is the pen drive dead ????
at 8:42 AM Posted by Sni
Similar solution if your pen drive is not visible in My Computer .
Solution :- Go to My computer .
Right Click and click on manage.
Computer Management window opens.
Click on storage.
Click Disk Management.
You can see your pen drive here.
Format it with FAT32.
Even now if u cannot see your pen drive on my computer or it does not opens , then your pen drive is dead.
Labels: Queries here 0 comments
PC hangs and restarts automatically !!!
at 8:37 AM Posted by Sni
Similar errors :-
1) PC hangs and display error - display driver has stopped working normally. To work properly go for restart.
2) Boot Disk Error.
Solution :-
May be your hide drive is faulty.Run software Speedfan which has hard drive health utility . ALso you can download bootable disc called Ultimate Boot CD and boot from it and run some more checking utilities.
These will detect if there is any problem with the hard disk.
Labels: Queries here 0 comments
XP doesn't shows more than 3.25 GB RAM for 4GB Configuration ???
at 8:33 AM Posted by Sni
Such type of limitation is faced by 32 -bit operating systems.Install a 64 - bit windows XP and you will be able to use all 4GB.
Labels: Queries here 0 comments
Fingerprint Scanners for Security !!!
at 1:54 AM Posted by Sni
Computerized fingerprint scanners have been a mainstay of spy thrillers for decades, but up until recently, they were pretty exotic technology in the real world. In the past few years, however, scanners have started popping up all over the place -- in police stations, high-security buildings and even on PC keyboards. You can pick up a personal USB fingerprint scanner for less than $100, and just like that, your computer's guarded by high-tech biometrics. Instead of, or in addition to, a password, you need your distinctive print to gain access.
A fingerprint scanner system has two basic jobs -- it needs to get an image of your finger, and it needs to determine whether the pattern of ridges and valleys in this image matches the pattern of ridges and valleys in pre-scanned images. There are a number of different ways to get an image of somebody's finger. The most common methods today are optical scanning and capacitance scanning. Both types come up with the same sort of image, but they go about it in completely different ways.
Optical Scanners
at 1:54 AM Posted by Sni
The heart of an optical scanner is a charge coupled device (CCD), the same light sensor system used in digital cameras and camcorders. A CCD is simply an array of light-sensitive diodes called photosites, which generate an electrical signal in response to light photons. Each photosite records a pixel, a tiny dot representing the light that hit that spot. Collectively, the light and dark pixels form an image of the scanned scene (a finger, for example). Typically, an analog-to-digital converter in the scanner system processes the analog electrical signal to generate a digital representation of this image. See How Digital Cameras Work for details on CCDs and digital conversion.
The scanning process starts when you place your finger on a glass plate, and a CCD camera takes a picture. The scanner has its own light source, typically an array of light-emitting diodes, to illuminate the ridges of the finger. The CCD system actually generates an inverted image of the finger, with darker areas representing more reflected light (the ridges of the finger) and lighter areas representing less reflected light (the valleys between the ridges).
Before comparing the print to stored data, the scanner processor makes sure the CCD has captured a clear image. It checks the average pixel darkness, or the overall values in a small sample, and rejects the scan if the overall image is too dark or too light. If the image is rejected, the scanner adjusts the exposure time to let in more or less light, and then tries the scan again.
If the darkness level is adequate, the scanner system goes on to check the image definition (how sharp the fingerprint scan is). The processor looks at several straight lines moving horizontally and vertically across the image. If the fingerprint image has good definition, a line running perpendicular to the ridges will be made up of alternating sections of very dark pixels and very light pixels.
If the processor finds that the image is crisp and properly exposed, it proceeds to comparing the captured fingerprint with fingerprints on file.
Capacitive Scanners
at 1:45 AM Posted by Sni
Like optical scanners, capacitive fingerprint scanners generate an image of the ridges and valleys that make up a fingerprint. But instead of sensing the print using light, the capacitors use electrical current.
The diagram below shows a simple capacitive sensor. The sensor is made up of one or more semiconductor chips containing an array of tiny cells. Each cell includes two conductor plates, covered with an insulating layer. The cells are tiny -- smaller than the width of one ridge on a finger.
The sensor is connected to an integrator, an electrical circuit built around an inverting operational amplifier. The inverting amplifier is a complex semiconductor device, made up of a number of transistors, resistors and capacitors. The details of its operation would fill an entire article by itself, but here we can get a general sense of what it does in a capacitance scanner. (Check out this page on operational amplifiers for a technical overview.)
Like any amplifier, an inverting amplifier alters one current based on fluctuations in another current (see How Amplifiers Work for more information). Specifically, the inverting amplifier alters a supply voltage. The alteration is based on the relative voltage of two inputs, called the inverting terminal and the non-inverting terminal. In this case, the non-inverting terminal is connected to ground, and the inverting terminal is connected to a reference voltage supply and a feedback loop. The feedback loop, which is also connected to the amplifier output, includes the two conductor plates.
As you may have recognized, the two conductor plates form a basic capacitor, an electrical component that can store up charge (see How Capacitors Work for details). The surface of the finger acts as a third capacitor plate, separated by the insulating layers in the cell structure and, in the case of the fingerprint valleys, a pocket of air. Varying the distance between the capacitor plates (by moving the finger closer or farther away from the conducting plates) changes the total capacitance (ability to store charge) of the capacitor. Because of this quality, the capacitor in a cell under a ridge will have a greater capacitance than the capacitor in a cell under a valley.
To scan the finger, the processor first closes the reset switch for each cell, which shorts each amplifier's input and output to "balance" the integrator circuit. When the switch is opened again, and the processor applies a fixed charge to the integrator circuit, the capacitors charge up. The capacitance of the feedback loop's capacitor affects the voltage at the amplifier's input, which affects the amplifier's output. Since the distance to the finger alters capacitance, a finger ridge will result in a different voltage output than a finger valley.
The scanner processor reads this voltage output and determines whether it is characteristic of a ridge or a valley. By reading every cell in the sensor array, the processor can put together an overall picture of the fingerprint, similar to the image captured by an optical scanner.
The main advantage of a capacitive scanner is that it requires a real fingerprint-type shape, rather than the pattern of light and dark that makes up the visual impression of a fingerprint. This makes the system harder to trick. Additionally, since they use a semiconductor chip rather than a CCD unit, capacitive scanners tend to be more compact that optical devices.
Labels: conceptual, windows 0 comments

